The concept of working from home has been around since the 1960s, and it accelerated in the 2000s when technology like video conferencing, cloud computing, and mobile devices became commonplace.
Unsurprisingly, the COVID-19 pandemic normalized remote working on a massive scale, sparking what economists call the “work-from-home economy”. Post-pandemic, remote working continues to be in demand.
While remote working has numerous benefits, there is a dark side. Since remote working is isolated in nature without the physical presence of others for accountability, there is a high potential for unethical business practices to emerge within remote working environments.
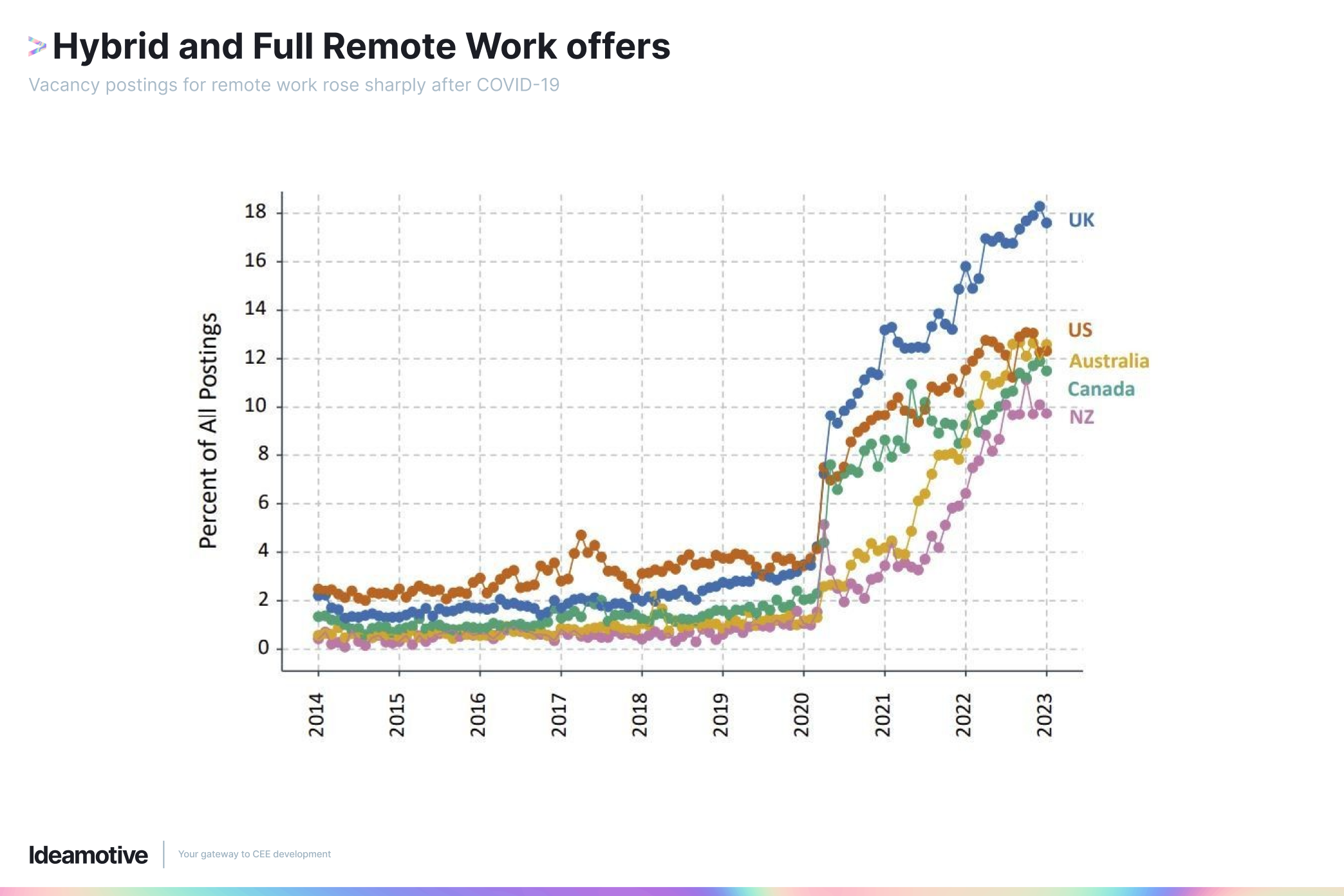
The IT sector is particularly vulnerable to these unethical business practices because, unlike industries such as tourism that require on-ground work, most IT jobs thrive in remote working conditions. In fact, a recent remote work report showed that IT jobs dominated the top five most popular remote job categories.
Thus, it is important for employers and employees in the IT sector to be aware of how unethical business practices can proliferate in remote working environments, learn how to address them, and take proactive steps to maintain a positive and ethical workspace.
Types of Unethical Business Practices in Remote IT Work
Unethical business practices can have a range of negative impacts on society, the economy, and the environment. Here are a few different kinds of unethical practices that can occur in the remote working environment.
- Employing underage workers
Child labor is a complex issue that can hurt society and the economy. It can perpetuate social inequalities, rob children of educational opportunities, and harm vulnerable populations living in poverty. In the short term, child labor may even lead to lower wages for adult workers.
Furthermore, the repercussions of being involved with hiring underage workers can be significant. For example, in the UK, anyone that employs children without proper authorisation can face fines of up to £20,000 per child. While in the US, those who violate child labor laws can face fines of up t $11,000 per violation.
Ethical businesses that never consider employing children may think they’re safe from these repercussions. However, in remote working conditions, ethical businesses can be inadvertently involved in child labor without their knowledge.
This can happen through third-party entities that position themselves as agencies on digital job boards or individuals with fake online profiles. Businesses that hire them may unknowingly hire an underage worker or collaborate with an agency that employs children.
- Sexual harassment in virtual environments
Sexual harassment can be more common in virtual environments because of the lack of face-to-face interaction, which can embolden the perpetrator when they think they can “get away with it.”
Sexual harassment can take many different forms in virtual environments, including unwanted sexual advances, comments, or gestures; the sending of sexually explicit materials or images; and the use of sexually explicit language in online communication.
This unacceptable behavior can have serious consequences for victims, including emotional distress, a hostile work environment, and negative impacts on job performance and productivity.
- Unfair competition and intellectual property theft
Unfair competition is a branch of intellectual property law. It refers to any illegal or unethical practices that lead to gaining an unfair advantage in the market. Some examples of unfair competition include false advertising, deception, fraud, stealing trade secrets, or oppression.
Intellectual property (IP) theft is a form of unfair competition that can significantly affect the IT sector. Software theft, illegal downloading, and piracy are widespread phenomena that can be difficult to detect and control.
Stealing trade secrets is another big issue in the IT industry. For example, a company or individual may steal a competitor's trade secrets by hacking into their computer systems, stealing their source code, or using social engineering tactics to access confidential information.
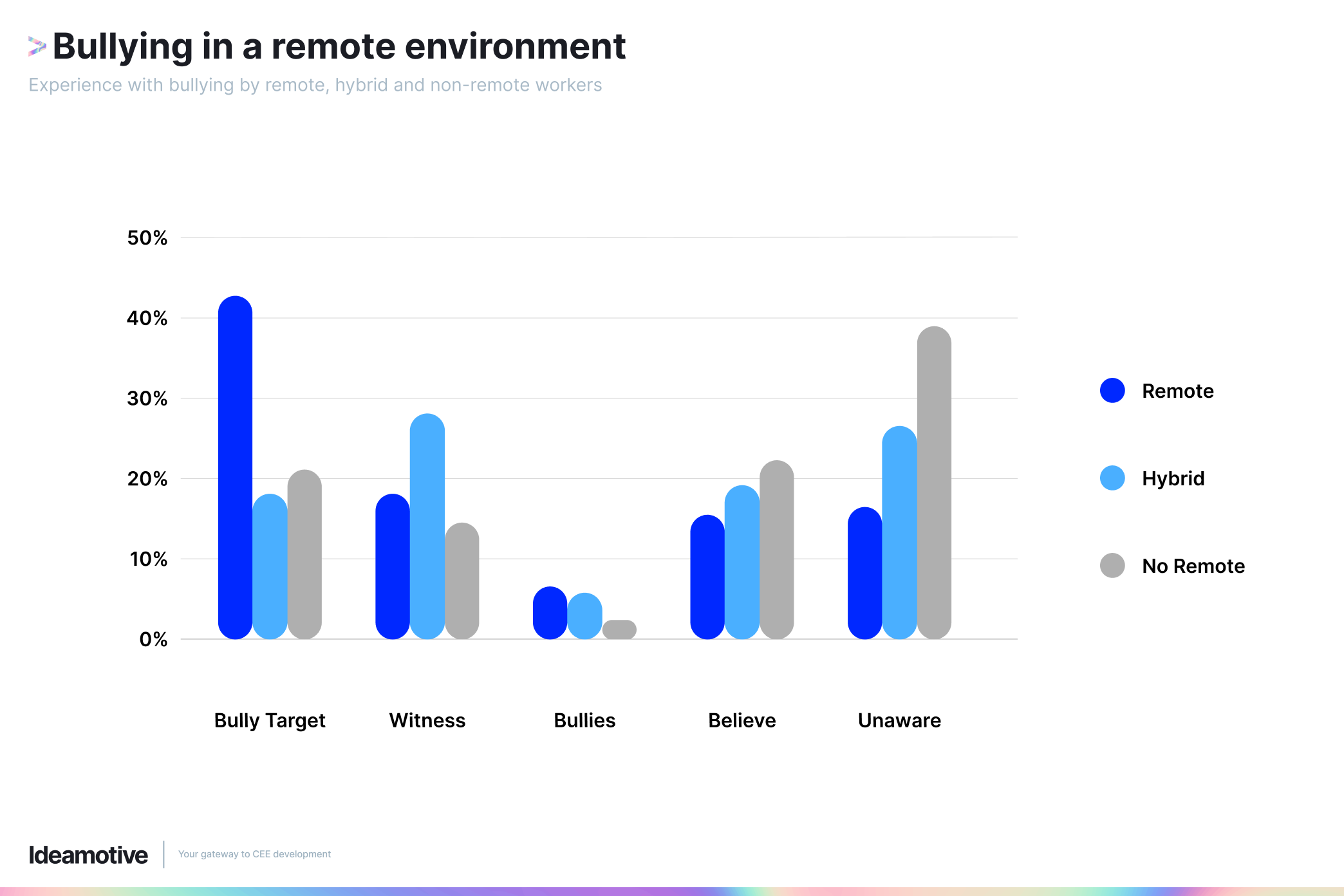
Alternatively, a company or individual may reverse engineer a program to reconstruct the source code and release a product almost exactly like a competitor's. Doing this without obtaining the necessary licenses or permissions violates copyright laws.
- Unethical practices related to environmental sustainability
Many environmental issues surround the production, operations, and disposal of the computing infrastructure that drives the IT sector.
Firstly, producing computing infrastructure such as servers, laptops, and other devices requires extracting raw materials, including rare earth metals, that are often mined in environmentally damaging ways.
Secondly, operating large-scale computing leaves behind a huge carbon footprint. For example, a 2016 report states that data centers are consuming about 3% of the global electricity supply and account for approximately 2% of total greenhouse gas emissions.
To put it in perspective, the IT industry’s greenhouse gas emissions are on par with the carbon footprint of the airline industry. It is also higher than the electricity consumption of the UK.
Finally, the disposal of computing infrastructure contributes to landfill waste. Approximately 50 million tons of electronic waste are dumped in landfills each year. The toxic heavy metals from computers can seep into the surrounding soil and contaminate the nearby groundwater.
- Bribery and Corruption in the digital sphere
The digital sphere has created new opportunities for bribery and corruption. For example, remote IT workers may be asked to manipulate online reviews or rankings so a company to gain an advantage over competitors.
Another form of corruption is providing the technology or skills that enable others to commit fraud, money laundering, or bribery. For example, a remote IT worker may develop software that facilitates illegal activities, or a company may bribe government officials to pass policies that give them an unfair advantage.
Case Study: Unethical Business Practices in Major Companies
Unfortunately, unethical business practices are prevalent across industries, and the IT sector is no exception. To ensure that ethical standards are upheld, proactive IT companies and professionals should take the initiative to learn from the experiences of other industries and cases.
Coca-Cola’s controversial history is one such example that the IT sector can learn from. Despite being one of the globe’s most recognizable brands, the company has been embroiled in numerous unethical business practices and faced multiple lawsuits.
Some of the biggest ethical crises associated with Coca-Cola include labor and human rights violations, health and environmental damage, and unethical marketing practices to gain an unfair advantage.
- Labor and human rights violations
Coca-Cola has faced allegations of labor rights violations in several countries, including using violence and causing the death of trade union leaders in Colombia and the wrongful termination of 105 employees in Turkey for their union activities.
In 1999, over 2,000 current and former African American employees sued Coca-Cola for racial discrimination. Plaintiffs stated that the company grouped African American workers at the bottom of the pay scale, earning them $26,000 less per year than their Caucasian colleagues.
- Controversies with health and environmental damage
In 1999, around 30 Belgian children became ill after consuming Coke products. After an isolated product recall, they determined that an improperly processed batch of carbon dioxide caused the illnesses. Coca-Cola was slow to respond to the problem and address the media.
Then in 2003, extreme levels of pesticides were found in Coca-Cola’s products in India. The toxic content was caused by using contaminated groundwater. Tests conducted on the sludge produced at Coca-Cola’s Indian plants resulted in toxic results, indicating that the groundwater was being contaminated by improper wastewater management.
- Unethical marketing practices and fraud
Coca-Cola also battles consumer perceptions that its soft drinks contribute to obesity. As such, they have been involved in several unethical marketing practices to reverse this image.
One instance is their “Motherhood and Myth-Busting” campaign in Australia. In this campaign, the company admitted they did not disclose the caffeine levels of their product, Diet Coke, to position the beverage as healthy for children.
Another instance is their misleading marketing around their product, VitaminWater, which was marketed as healthy despite containing high sugar and lacking the nutritional requirement to make health claims.
Coca-cola has also been accused of fraud by channel stuffing in the early 2000s. Channel stuffing involves shipping unrequested inventory to wholesalers at the end of a quarter and refunding the returns later. This practice allows them to count the extra shipment as revenue at the end of the quarter, resulting in inflated financial statement earnings and misleading investors.
These unethical practices have impacted Coca-Cola’s bottom line numerous times. For example, Coca-Cola’s slow response to address the processing issues in Belgium escalated into a public relations nightmare that severely harmed its reputation, while the groundwater contamination incident in India led to a 15% drop in sales.

Coca-Cola’s bottom line has also been impacted by millions of dollars in settlements related to various legal disputes and controversies. Its false advertising of VitaminWater cost them a $2.7 million settlement, while its discrimination against African American employees cost them $193 million in settlements.
By learning from the past mistakes of companies like Coca-Cola, the IT industry can take proactive steps to prevent and address unethical business practices, particularly in the remote working environment.
Addressing Unethical Business Practices in Remote IT Work
Unethical business practices can be detrimental to the reputation and sales of any organization. Here are several strategies that IT companies can implement to minimize unethical practices in their remote working environments.
- Creating clear guidelines and policies on ethical conduct
- Provide easy access to guidelines and policy documentation that states the organization’s culture and ethical boundaries.
- Define the culture and expected behavior of employees or contractors and the types of behavior that will not be tolerated.
- State clearly and simply how employees or contractors should communicate with each other and what topics are taboo.
- Encouraging open communication and reporting unethical behaviors
- Set an example by openly communicating the types of misconduct, harassment, and unethical behaviors that will not be tolerated.
- Provide easy channels for people to report unethical behaviors without fear of repercussions.
- Protect whistleblowers with policies such as anonymous reporting and confidentiality agreements.
- Implementing robust systems for monitoring and ensuring compliance
-
- Implement an effective whistleblowing system and regular audits to identify and address unethical practices.
- Uphold best practices in responsible supply chain management, such as transparency and accountability.
- Uphold best practices in green computing, also known as green IT, to design, develop, use, and dispose of computing resources in an environmentally friendly way.
- Promoting a culture of ethical responsibility and accountability
-
- Foster a culture of trust through online team-building activities and meetings that build interpersonal relationships in remote working conditions.
- Recognize and reward ethical behavior through incentives such as bonuses and cashless recognition such as awards and thank you letters.
- Clearly communicate your company values and demonstrate how ethics are integrated into the mission.
The Role of Management in Combating Unethical Business Practices
Management is crucial in leading by example to set a high ethical standard. Their compliance with ethics in the workplace sets the tone for the rest of the company. If leaders act unethically, then company policies can just become lip service.
It is also important for IT managers and team leaders to create a supportive and inclusive work environment. This includes hiring a diverse team, being open to receiving criticism and taking accountability.
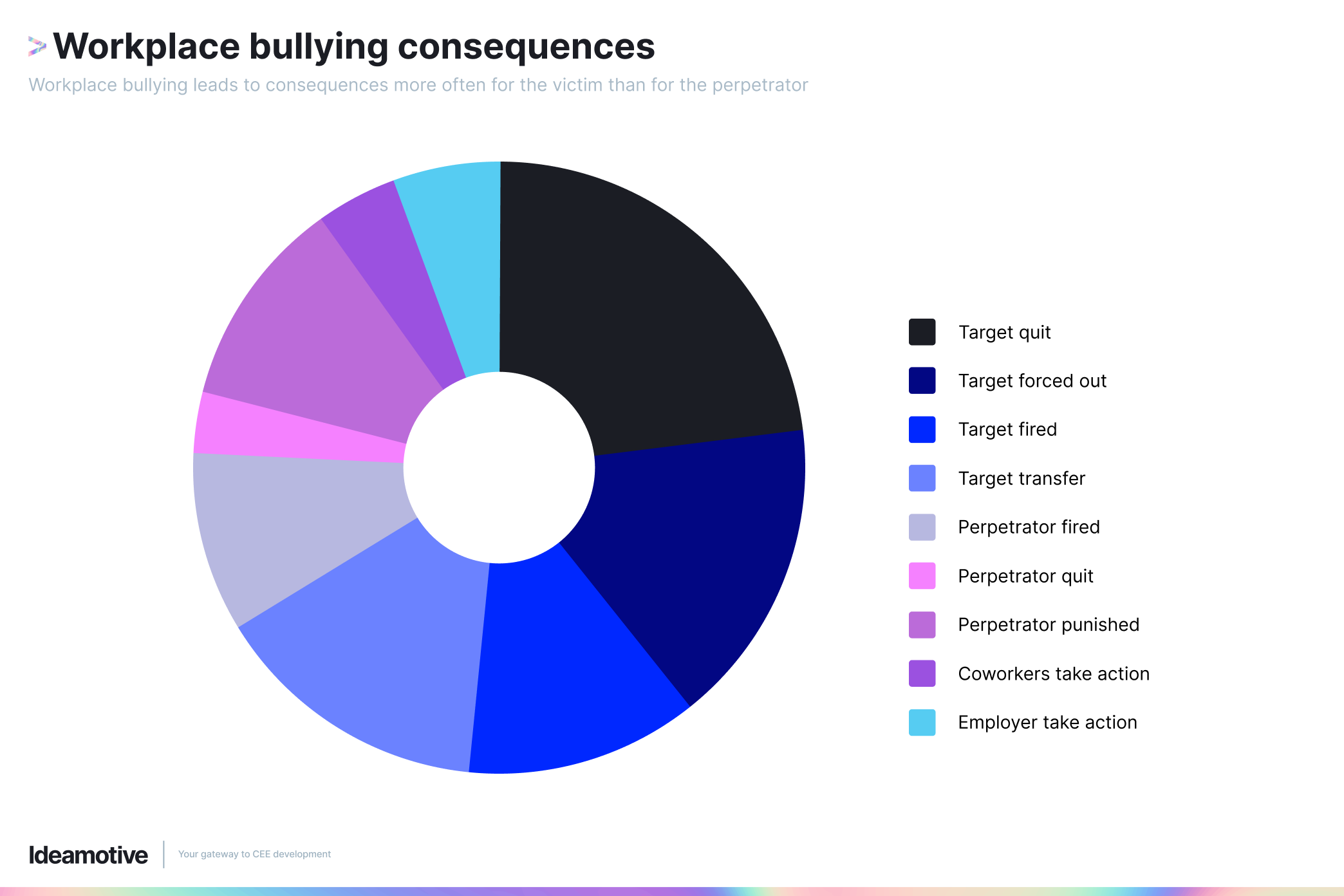
Management in the IT sector can also invest in tools and technology to facilitate ethical practices, such as compliance management software, carbon footprint calculators, and anti-bribery and corruption tools.
Remote working in the IT sector has presented its ethical dilemmas. Understanding and tackling these concerns is essential, as it can impact the IT sector’s reputation.
To achieve an ethical remote work environment, IT companies must have strong management, clear policies, and a unified dedication to integrity and trust. Management and leadership teams of companies must unite their efforts to build up a culture of ethical responsibility and accountability.
Management should also strive to prioritize best practices in ethical business over short-term gain since unethical business practices have been shown to impact the bottom line, ruin a company’s image, or lead to costly lawsuits.
By implementing ethical business practices and learning from the past mistakes of unethical companies, the IT sector can thrive sustainably and foster a positive impact on society and the environment.