Software investments can be complex yet, significant. Private equity firms' investments in software have performed exceptionally well, outpacing other investments made by the asset class for more than a decade. There were over 500 deals in the software industry with a combined value of more than $100 billion in 2022. So, IT leaders need to ensure that the software purchases match the company's business goals and technology infrastructure. One way to achieve this alignment is through due diligence. Let’s check the importance of assessing software investments with our due diligence guide for IT leaders, including evaluation steps and possible pitfalls to avoid.
What Makes Software Due Diligence So Important for IT Management?
We all witness how technology becomes more intricate and intertwined with our lives. So, it remains a crucial component in driving business growth and transformation. How software due diligence works for mergers, acquisitions, and sales has changed because business transformation is ever-evolving. Therefore, the acquirer must remain vigilant in assessing all potential risks to succeed.
Due diligence is used to find business and technology risks, and its results are significant for figuring out a transaction's costs, investments, and opportunities. Additionally, it provides valuable information on growth and scalability for companies. There are many due diligence types you can learn about.
We try to clarify here what makes a well-defined and structured due diligence process essential to the investment strategy:
- Safeguard compliance: Companies must comply with regulatory requirements. There are technology vendors that fail to meet these standards;
- Sensitive information protection: Check if the company handles confidential clients, making it crucial to ensure that technology vendors have appropriate information security measures in place to safeguard this data;
- Uphold the company's reputation: Investment in technology vendors that do not adhere to industry standards or have a track record of security breaches can harm your company's reputation;
- Secure financial interests: Utilizing unreliable or unsecured technology can lead to costly disruptions and downtime, potentially affecting the financial performance of your company negatively;
- Ensure vendor reliability: Conducting comprehensive due diligence on technology vendors can assist the company in evaluating the vendor's financial stability and long-term viability.
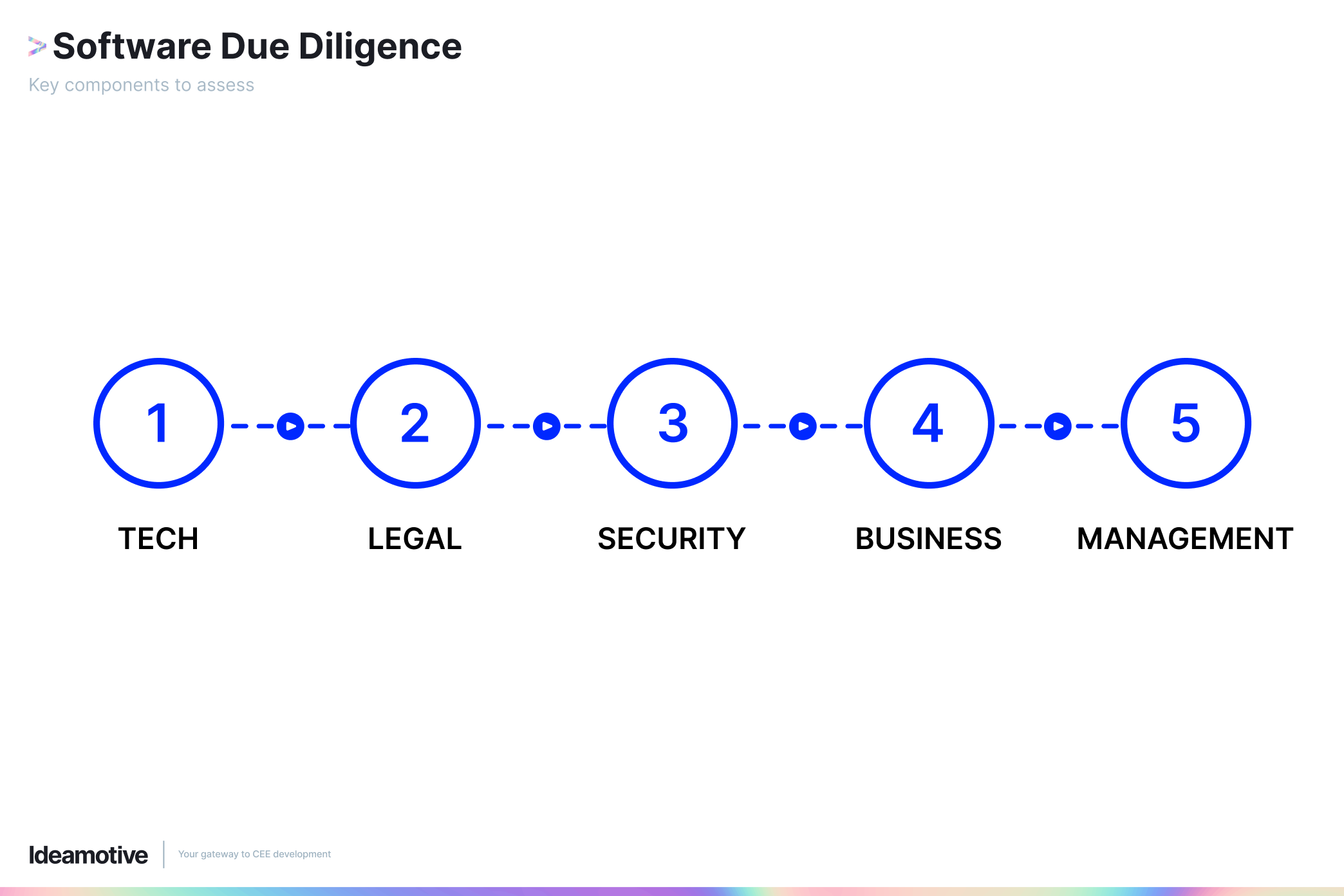
Key Components of Due Diligence for IT Projects
This evaluation process for IT investments helps understand the feasibility and risks associated with a potential investment. It involves a thorough analysis of the investment target project, or we will call it below “target company”, to see if it fits with the goals and needs of your company.
You need to look at some vital areas to make a successful evaluation. For example, people working on a project, their knowledge, skills, and experience, and how they supervise or manage the workflow. You should also examine the project's technology: originality, code quality, a competitive edge, and intellectual property rights.
The key components of due diligence you should outline in your report are as follows:
- Business assessment
The primary component is to conduct a business assessment to determine the feasibility of the investment. This includes assessing the target company's financial performance, market position, and growth potential. It is also worth looking at the business model, product roadmap, and competitive landscape of the target company to see if they fit in with your business's goals and needs;
- Technical assessment
The technical assessment evaluates the target company's technology and infrastructure to determine its capabilities and limitations. This includes assessing the software systems, hardware, AI implementation in business, and network infrastructure. The technical assessment should also look at the technology roadmap of the project to see if it fits with the goals and needs of your business;
- Security assessment
In this assessment, the security posture of the target company is looked at to see how well it can protect itself from cyber threats, it covers:
- checking security policies and procedures;
- the safety of its network;
- the privacy of its data;
- how well it follows industry standards and rules.
The security assessment should also cover the risk management processes and procedures. It helps ensure they fit with your company's risk appetite.
- Legal assessment
In the legal and compliance assessment, the legal and regulatory compliance of the target company is looked at to see if it meets industry standards and rules. That concerns looking at the contracts, intellectual property, and compliance with the laws and rules.
- Management Assessment
It involves evaluating the target company's management team. It covers the target company's management structure, employee retention rates, and engagement of employees. The management assessment should also examine how well the target company fits your business's values and culture.
10 Steps of Conducting Software Due Diligence
Investing in software without proper due diligence can lead to financial loss, data breaches, and missed opportunities. We offer our guide that will enable you to make informed decisions and select software to help your business grow.
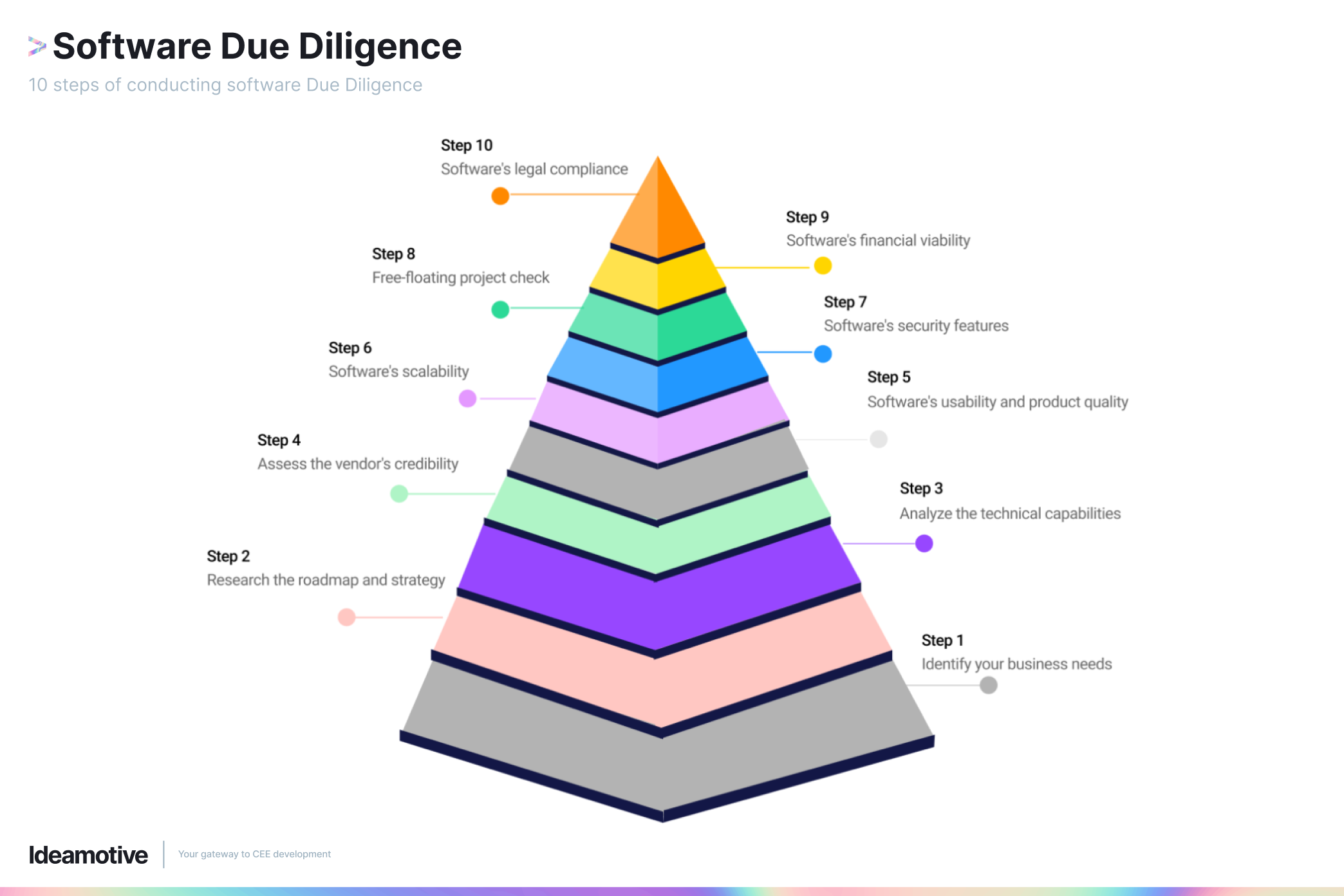
Step 1: Identify your business needs
You should study your current business processes, identify gaps, and determine what software features meet your needs. In addition, you should consider factors such as cost, scalability, user-friendliness, and integration capabilities.
Step 2: Research the roadmap and strategy
After figuring out your business demands, research the roadmap and product strategy to determine the available options that meet your requirements:
- Providing full SWOT awareness and inclusion in the roadmap;
- Ensuring alignment and collaboration with the business roadmap and strategy;
- Confirming the existence, documentation, and propagation of a reasonable roadmap;
- Evaluating the feasibility of executing the roadmap by the team;
- Determining the ability to address market needs with clarity on product/service gaps;
- Conducting a deep dive into the product strategy, including how technology evolves;
- Analyzing the execution discipline and maturity, such as backlog epics and backlog health.
Step 3: Analyze the software's technical capabilities
It would help if you explored the end-to-end architecture's suitability for the current business, design efficiency, stability, ability to evolve and stay competitive, and whether it fits your investment strategy:
- Examining the architecture design patterns, robustness, limitations, and roadblocks;
- Understanding the maintainability process for the architecture and codebase;
- Determining the scalability strategy, regulations, and performance with KPIs;
- Exploring the levels of technical debt and management approach;
- Ensuring security design, vulnerabilities, fraud detection and secure programming principles are in place;
- Analyzing the integrations and extensibility of the architecture;
- Reviewing the data architecture and management lifecycle, including collection and cleansing;
- Examining the database and data security, including handling of sensitive data, encryption, etc.;
- Ensuring open-source usage, licensing, and intellectual property ownership complies;
- Analyzing quality processes and ability to deploy and time to market;
- Following cloud readiness best practices.
Step 4: Assess the vendor's credibility and customer support
The credibility of the vendor is crucial when investing in software. You should research the vendor's background, financial stability, and reputation in the market. It would help if you also considered customer support, training, and maintenance services. It is good to ask the vendor's existing clients to assess their satisfaction levels:
- Examining the end-to-end customer support process;
- Determining defect rates and management process;
- Analyzing escalation rates and management process;
- Delineating between support and engineering responsibilities;
- Ensuring the support tools ecosystem is adequate and rationalized;
- Gathering feedback on the product.
Step 5: Evaluate the software's usability and product quality
You should test the user interface, navigation, or user experience. So, conduct a usability test to assess how the software functions in real-world scenarios:
- Examining the approach to testing and quality assurance;
- Ensuring the level of automation, code coverage, and ability to catch bugs upstream;
- Reviewing the test case management process and tools;
Step 6: Analyze the software's scalability
The scalability of the product is essential to encompass your business’s growth. Therefore, consider the software's capacity, performance, and ability to handle increased user traffic. In addition, we advise analyzing the software's architecture and infrastructure to determine its scalability.
Step 7: Verify the software's security features
Try to give thorough attention to security and privacy as a complete layer end-to-end, including design, controls, practices, policies, vulnerability detection, mitigation, and implementation. Focus on:
- Reviewing policies and procedures;
- Analyzing security controls;
- Ensuring security education is provided;
- Reviewing inventory and ownership;
- Ensuring data privacy and security policies comply with regulations such as PCI, PHI, PII, and GDPR;
- Analyzing data storage and access permissions;
- Ensuring infrastructure security;
- Reviewing the monitoring and intrusion detection strategy;
- Ensuring the physical security strategy is in place;
- Examining the history of breaches and their management;
- Confirming compliance requirements and domain-specific compliance needs are met.
Step 8: Free-floating project check
You should explore the ability of the project to function as a stand-alone entity and understand end-to-end capabilities, intellectual property ownership, and dependencies. To prepare, focus on:
- Analyzing the project’s chart after the split;
- Determining roles and responsibilities;
- Ensuring there is no line of business tools dependencies;
- Identifying security gaps;
- Ensuring hosting and deployment independence;
- Analyzing contractual agreements and IP concerns.
Step 9: Review the software's financial viability
The financial viability of the vendor is crucial to ensuring that they can sustain their business operations and support the software's development. You should review the vendor's financial statements, cash flow, and funding sources. Assessing the vendor's growth potential and expansion plans is also advisable.
Step 10: Verify the software's legal compliance
Investing in software involves compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements, such as data protection laws, intellectual property rights, and software licenses. You should verify that the software meets these requirements and that you have the necessary licenses and agreements.
How to Avoid Common Pitfalls
Now that we’ve offered a tech due diligence checklist, let's look at what general mistakes can lead to your investment not living up to expectations:
Pitfall 1: Not defining your requirements
One of the biggest mistakes you can make is not defining your requirements before starting the due diligence process. With a clear idea of what you need, comparing software solutions and choosing the right one can be easy.
Pitfall 2: Over-reliance on vendor information
IT leaders should use more than just vendor information when evaluating possible software solutions. Independent evaluations and assessments should also be conducted. It's essential to look beyond the vendor's website and do research to learn about their track record, reputation, and customer reviews.
Pitfall 3: Failure to identify potential risks
IT leaders should thoroughly assess the product to determine if it poses any risks. Please do so to avoid costly mistakes and negative consequences.

Pitfall 4: Failure to conduct due diligence before investing
Another common pitfall is a failure to conduct proper due diligence. First, businesses should conduct due diligence before investing in IT. It includes researching the market, analyzing technical capabilities, figuring out how trustworthy the vendor is, and figuring out how easy the software is to use and how well it can grow.
Pitfall 5: Focusing solely on features and functionalities
Even though features and functions are essential, it's also important to think about things like performance, security, and the ability to grow. A software solution may have all the features you need, but it may fit your needs better if it needs to be more secure and scalable.
Pitfall 6: Studying contracts and licensing agreements, paying no attention to details
Finally, it's important to review contracts and licensing agreements thoroughly. Ensure that the terms and conditions are clear. There should be no hidden costs or restrictions that could affect your decision.
Summary
Software investments can affect the company's lifecycle, making due diligence essential for IT leaders. Due diligence process involves investigating and evaluating software to identify potential risks and ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
When investors do their due diligence, they get a complete picture of whether it's worth taking a risk and completing a deal or whether they should look for a more reliable business partner to work with. It is also utilized to evaluate the potential profitability of project implementation and assess the risks associated with the process. This approach identifies potential market barriers and aids in selecting the most appropriate business model for software distribution or the commercialization of software within specific market segments.
It is vital to stress that the analysis must give reliable and unbiased information to everyone involved. To achieve this, you should enlist the services of an independent, external company to carry out the research.